Now that we’re approaching the end of the year, it’s time to review your business finances. We’ve highlighted the most critical tax-planning tips you need to know as a business owner.
Salary/Dividend Mix
As a business owner, an essential part of tax planning is determining if you receive salary or dividends from the business.
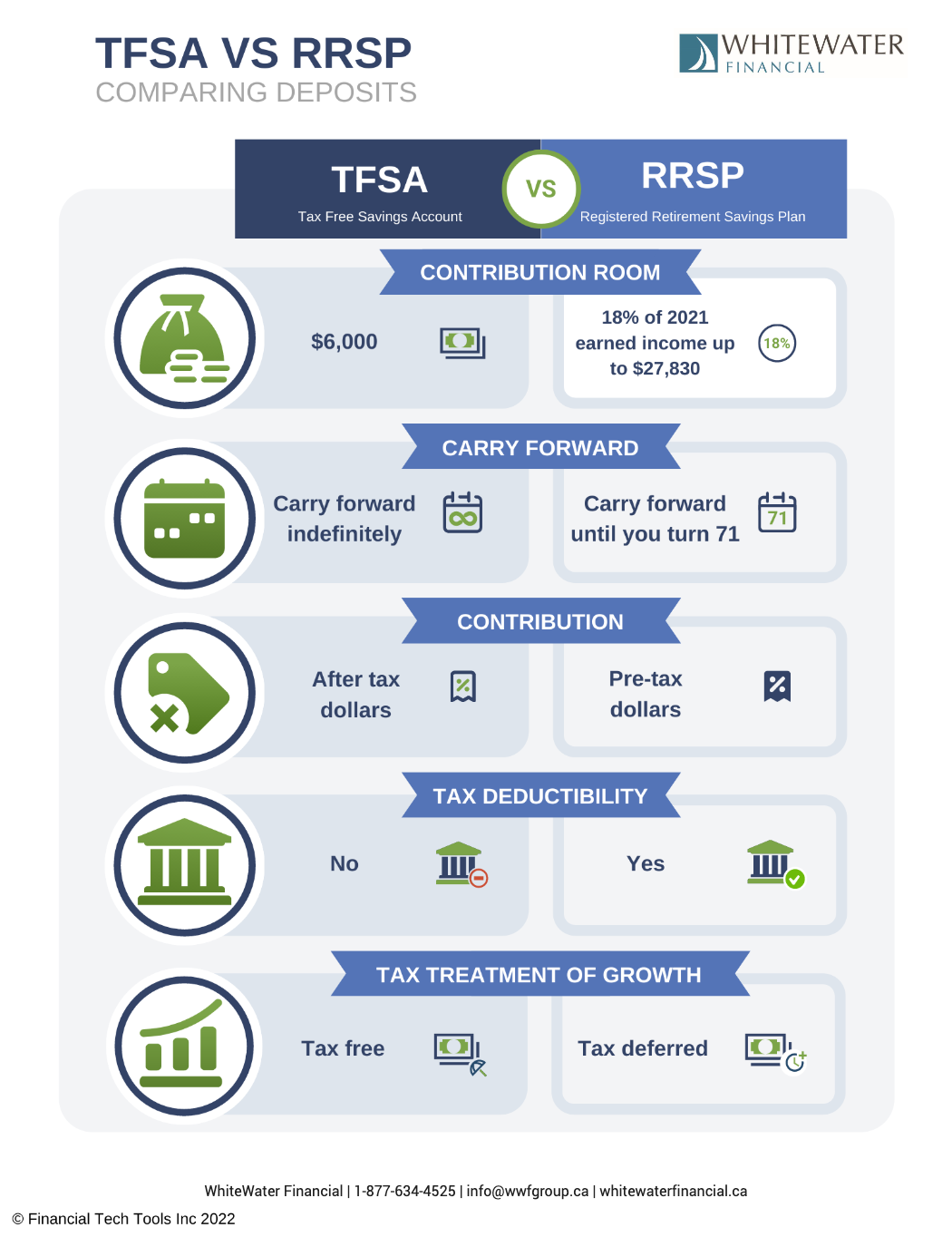
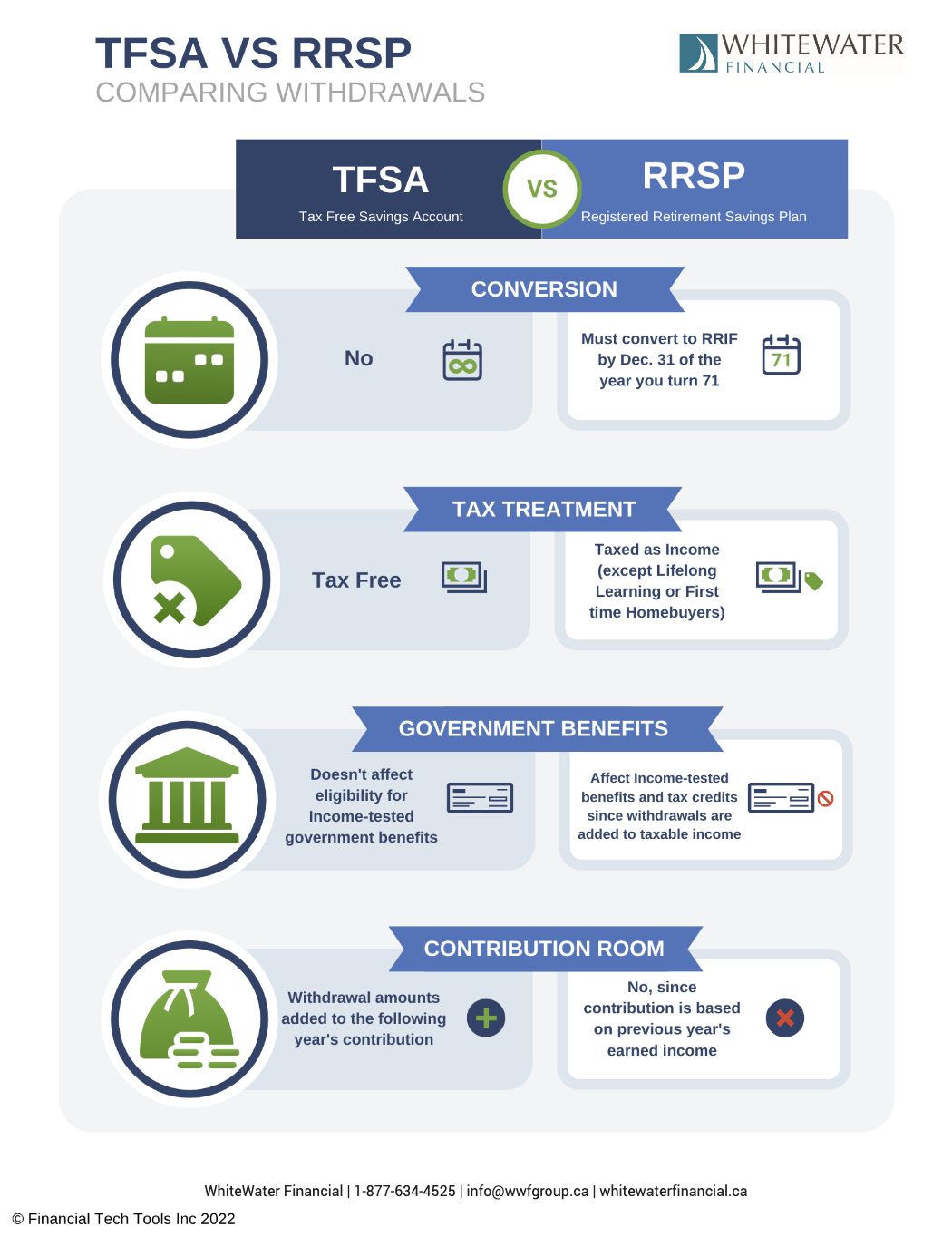
When you’re paid a salary, the corporation can claim an income tax deduction, which reduces its taxable income. You include this pay in your personal taxable income. You’ll also create Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) contribution room.
The alternative is the corporation can distribute a dividend to you. The corporation must pay tax on its corporate income and can’t claim the dividend distributed as a deduction. However, because of the dividend tax credit, the dividend typically pays a lower tax rate (than for salary) on eligible and non-eligible dividends.
In addition to paying yourself, you can consider paying family members. These are the main options you can consider when determining how to distribute money from your business:
-
Pay a salary to family members who work for your business and are in a lower tax bracket. This enables them to declare an income so that they can contribute to the CPP and an RRSP. You must be able to prove the family members have provided services in line with the amount of compensation you give them.
-
Pay dividends to family members who are shareholders in your company. The amount of dividends someone can receive without paying income tax on them will vary depending on the province or territory they live in.
-
Distribute money from your business via income sprinkling, which is shifting income from a high-tax rate individual to a low-rate tax individual. However, this strategy can cause issues due to tax on split income (TOSI) rules. A tax professional can help you determine the best way to “income sprinkle” so none of your family members are subject to TOSI.
-
Keep money in the corporation if neither you nor your family members need cash. Taxes can be deferred if your corporation retains income and the corporation’s tax rate is lower than your tax rate.
No matter what strategy you take to distribute money from your business, keep in mind the following:
-
Your marginal tax rate as the owner-manager.
-
The corporation’s tax rate.
-
Health and payroll taxes
-
How much RRSP contribution room do you have?
-
What you’ll have to pay in CPP contributions.
-
Other deductions and credits you’ll be eligible for (e.g., charitable donations or childcare or medical expenses).

Compensation
Another important part of year-end tax planning is determining appropriate ways to handle compensation. Compensation is financial benefits that go beyond a base salary.
These are the main things to consider when determining how you want to handle compensation:
-
Can you benefit from a shareholder loan? A shareholder loan is an agreement to borrow funds from your corporation for a specific purpose and offers deductible interest.
-
Do you need to repay a shareholder loan to avoid paying personal income tax on your borrowed amount?
-
Is setting up an employee profit-sharing plan a better way to disburse business profits than simply paying a bonus?
-
Keep in mind that when an employee cashes out a stock option, only one party (the employee OR the employer) can claim a tax deduction on the cashed-out stock option.
-
Consider setting up a retirement compensation arrangement (RCA) to help fund your or your employee’s retirement.
Passive Investments
One of the most common tax advantages available to Canadian-controlled private corporations (CCPC) is the first $500,000 of active business income in a CCPC qualifies for the small business deduction (SBD), which reduces the corporate tax rate by 12 to 21 percent, depending on the province or territory.
With the SBD, you can reduce your corporate tax rate, but remember that the SBD will be reduced by five dollars for every dollar of passive investment income over $50,000 your CCPC earned the previous year.
The best way to avoid losing any SBD is to ensure that the passive investment income within your associated corporation group does not exceed $50,000.
These are some of the ways you can make sure you preserve your access to the SBD:
-
Defer the sale of portfolio investments as necessary.
-
Adjust your investment mix to be more tax efficient. For example, you could hold more equity investments than fixed-income investments. As a result, only 50% of the gains realized on shares sold are taxable, but investment income earned on bonds is fully taxable.
-
Invest excess funds in an exempt life insurance policy. Any investment income earned on an exempt life insurance policy is not included in your passive investment income total.
-
Set up an individual pension plan (IPP). An IPP is like a defined benefit pension plan and is not subject to the passive investment income rules.

Depreciable Assets
Consider speeding up the purchase of depreciable assets for year-end tax planning. A depreciable asset is a capital property on which you can claim Capital Cost Allowance (CCA).
Here’s how to make the most of tax planning with depreciable assets:
-
Make use of the Accelerated Investment Incentive. This incentive makes some depreciable assets eligible for an enhanced first-year allowance.
-
Purchase equipment such as zero-emissions vehicles and clean energy equipment eligible for a 100 percent tax write-off.
-
Consider postponing the sale of a depreciable asset if it will result in recaptured depreciation for your 2022 taxation year.
Qualified Small Business Corporation (QSBC) Share Status
Ensure your corporate shares are eligible to get you the $913,630 (for 2022) lifetime capital gains exemption (LCGE). The LCGE is $1,000,0000 for dispositions of qualified farm or fishing property.
Suppose you sell QSBC shares scheduled to close in late December 2022 to January 2023. In that case, you may want to consider deferring the sale to access a higher LCGE of $971,190 for 2023 and therefore defer the tax payable on any gain arising from the sale.
Consider taking advantage of the LCGE and restructuring your business to multiply access to the exemption with other family members. But, again, you should discuss this with us, your accountant and legal counsel to see how this can benefit you.
Donations
Another essential part of tax planning is to make all your donations before year-end. This applies to both charitable donations and political contributions.
For charitable donations, you need to consider the best way to make your donations and the different tax advantages of each type of donation. For example, you can:
-
Donate Securities
-
Give a direct cash gift to a registered charity
-
Use a donor-advised fund account at a public foundation. A donor-advised fund is like a charitable investment account.
-
Set up a private foundation to solely represent your interests.
We can help walk you through the tax implications of these types of charitable donations.
Get year-end tax planning help from someone you can trust!
We’re here to help you with your year-end tax planning. So book a meeting with us today to learn how you can benefit from these tax tips and strategies.