With the upcoming 2024 Canadian tax rule changes, it’s important to review your financial strategies. We’ve identified the key changes that we expect to influence financial decisions for investors, business owners, incorporated professionals, retirees, and individuals with high income or net worth.
Capital Gains Inclusion Rate
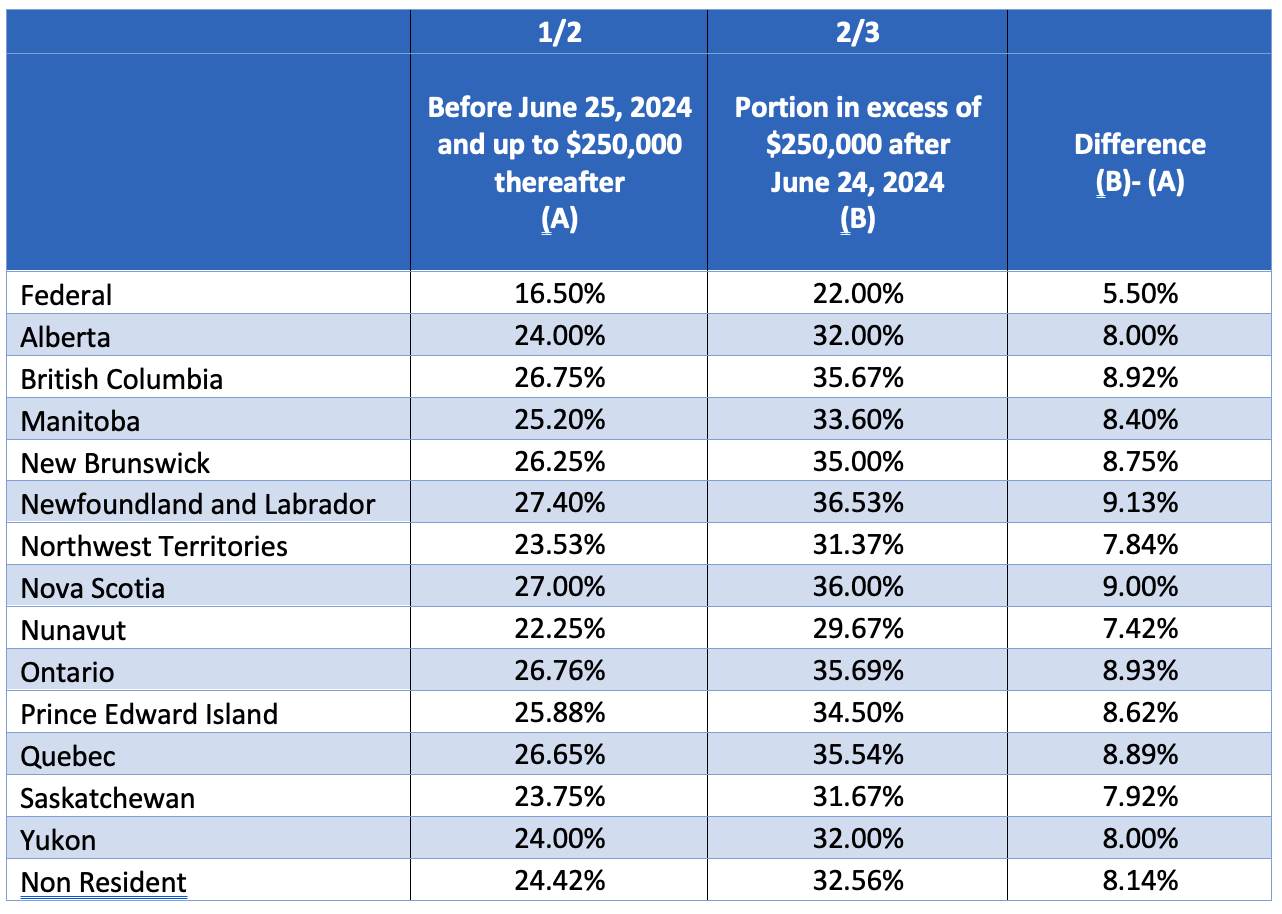
Starting on June 25, 2024, the tax on capital gains is changing. Until now, you would only have to include half of your capital gains in your income for tax purposes. But after that date, you’ll have to include two-thirds of any capital gains over $250,000 on your tax return. This is also the case for employee stock options.
Consequently, for corporations and trusts, they will have to include two-thirds of all their capital gains, no matter the amount. This is a significant change.
Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption (LCGE)
The budget proposes increasing the LCGE for qualified capital gains from $1,016,836 to $1.25 million, effective for sales made after June 24, 2024. This change increases tax benefits for individuals selling certain types of property, such as small business shares or farming and fishing assets.
Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)
The 2023 budget included updates to the AMT, suggesting revising the charitable donation tax credit for AMT calculations, increasing the claimable amount from 50% to 80%.
Employee Ownership Trust (EOT)
The budget proposes a tax exemption on up to $10 million in capital gains for individuals selling their businesses to an EOT if certain criteria are met.
Canadian Entrepreneurs’ Incentive
This new tax measure offers a reduced inclusion rate of 1/3 for up to $2 million in capital gains during an individual’s lifetime, with this limit being phased in over 10 years. However, it’s important to know that not all businesses qualify—this doesn’t apply to businesses in professional services, finance, real estate, hospitality, arts, entertainment, or personal care.
Below is a checklist to help you navigate the tax adjustments and ensure your financial plans are updated and aligned with the new rules.
Investors
-
Investments: Evaluate portfolios to identify where capital gains can be realized under the current lower inclusion rate.
-
Investment Property: Consider advancing the sale of such properties to benefit from the existing capital gains rate.
-
Estate Planning: Revise plans to address potential increases in capital gains taxes, ensuring estates are structured for tax efficiency.
-
Employee Stock Options: Adjust the timing of exercising stock options to align with the upcoming changes in inclusion rates.
Business Owners:
-
Corporate Investments: Assess the impact of increased inclusion rates on corporately held assets, exploring the timing of gains realization. Review trust-held investments.
-
Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption: Maximize the benefits of the increased LCGE for qualifying business assets.
-
Employee Ownership Trust: Consider the advantages of transferring business ownership via an EOT.
-
Succession Planning: Update your succession plans to consider the potential impact of capital gains tax changes.
-
Entrepreneurs Incentive: Check if you are eligible to reduce capital gains taxes.
Incorporated Professionals:
-
Investments: Assess both personal and corporate investments for the new inclusion rate. Determine the most tax-effective structure for holding and realizing gains from investments.
-
Succession Planning: Time the potential sale of your professional corporation to capitalize on the current LCGE.
Retirees:
-
Estate Planning: Update estate plans considering the impending increase in capital gains rates.
-
Life Insurance Coverage: Ensure life insurance is adequate to cover increased capital gains tax liabilities upon death.
-
Non-Registered Investments and Retirement Income: Review your strategy for non-registered investments to manage taxes on gains and adjust your retirement income plans to accommodate the upcoming changes in capital gains rates.
Individuals with High Income or Net Worth:
-
Investments: Evaluate portfolios to identify where capital gains can be realized under the current lower inclusion rate. Review trust-held investments.
-
Investment Property: Consider advancing the sale of such properties to benefit from the existing capital gains rate.
-
Estate Planning: Revise plans to address potential increases in capital gains taxes, ensuring estates are structured for tax efficiency.
-
Charitable Contributions: Align your charitable giving strategies with the new tax benefits and AMT considerations.
Please reach out to us to review your financial strategy together and ensure it aligns with the upcoming changes.